Introduction
This blog post from WildHawk Physical Therapy will introduce you to ACL tears. In this in-depth exploration, we will dive into the intricate world of ACL tears—the challenges they present and the viable path of non-operative management. Whether you’re an athlete grappling with this common injury or someone seeking a holistic approach to rehabilitation, understanding the nuances of non-operative strategies is essential for a comprehensive recovery.
Understanding ACL Tears: An Overview
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is a key stabilizing ligament in the knee, crucial for maintaining stability during movements like pivoting and sudden changes in direction. ACL tears often occur during sports or activities that involve rapid stops, twists, or jumps, leading to a range of symptoms such as pain, swelling, and a feeling of instability in the knee.
Diagnosing ACL Tears
The diagnosis of an ACL tear typically involves a thorough examination by a healthcare professional, including a review of medical history, a physical examination, and often imaging tests like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to confirm the extent of the injury. Traditionally, many ACL tears have been treated with surgical intervention; however, non-operative approaches have gained recognition as viable alternatives, particularly for certain individuals and situations.
Non-Operative Management: A Holistic Approach
Non-operative management of ACL tears involves a multifaceted approach aimed at addressing symptoms, restoring function, and preventing long-term complications. Let’s explore the key components of this holistic strategy:
Rehabilitation Exercises: Building Strength and Stability
One of the pillars of non-operative management is a targeted rehabilitation program. Physical therapists design exercises that focus on strengthening the muscles surrounding the knee, with an emphasis on the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles. These exercises not only contribute to overall leg strength but also help stabilize the knee joint, compensating for the absence of the ACL.
- Quadriceps Strengthening: Exercises such as leg presses, squats, and leg extensions target the quadriceps, promoting stability and support for the knee joint.
- Hamstring Strengthening: Hamstring exercises, including leg curls and deadlifts, play a crucial role in balancing muscle strength around the knee, enhancing stability.
- Proprioception and Balance Training: These exercises focus on improving proprioception, the body’s awareness of its position in space, and balance. Proprioceptive training helps individuals regain control over their movements, reducing the risk of further injury.
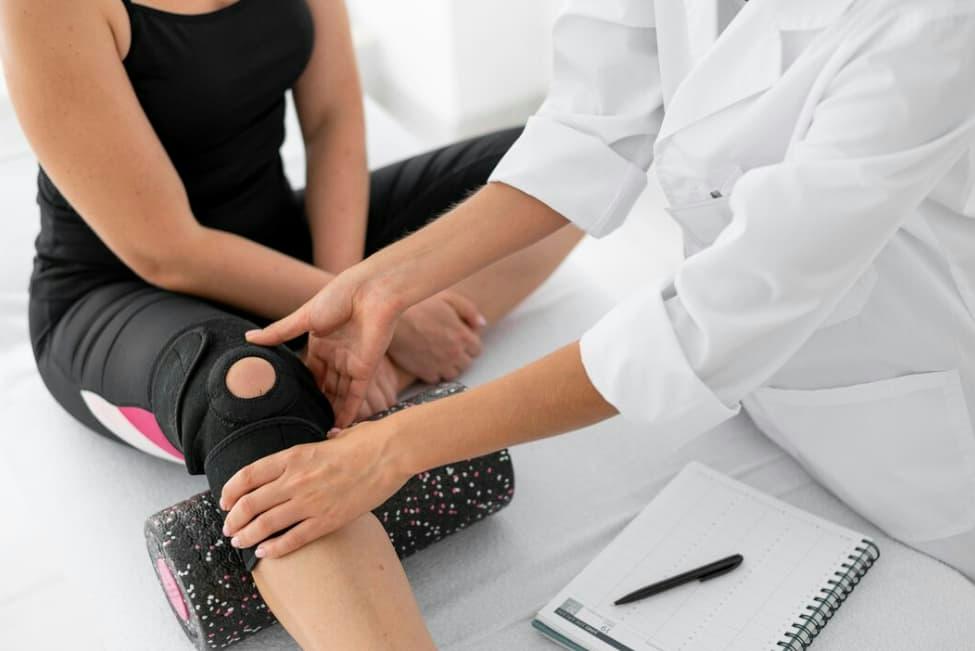
Bracing for Support
Knee braces can provide external support to the injured knee, helping to stabilize the joint during physical activities. While braces don’t replace the function of the ACL, they can offer a degree of protection and enhance confidence in movement.
- Functional Bracing: These braces are designed to provide support during specific activities, such as sports or strenuous physical tasks. They are often recommended for individuals who want to return to high-demand activities without surgery.
- Prophylactic Bracing: In some cases, individuals may wear braces to prevent injury, especially during activities with a higher risk of knee trauma. Prophylactic bracing is more common in certain sports or occupations.
Physical Therapy: Hands-On Intervention
Skilled physical therapists play a pivotal role in the non-operative management of ACL tears. They employ various hands-on techniques to enhance joint mobility, reduce pain, and address compensatory movements that may develop due to the injury.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques such as joint mobilization, soft tissue manipulation, and massage are used to improve knee joint mobility, alleviate pain, and enhance overall function.
- Range of Motion Exercises: Physical therapists guide individuals through specific exercises to restore and improve the range of motion in the knee joint. This is crucial for regaining flexibility and preventing stiffness.
- Gait Analysis: Analyzing the individual’s walking or running pattern helps identify any abnormal movements or compensations. Addressing these issues is essential for optimizing function and reducing the risk of secondary injuries.
Pain Management Strategies
Managing pain is an integral part of non-operative care, allowing individuals to engage actively in rehabilitation without undue discomfort. Various pain management strategies may be employed, depending on the severity of symptoms.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen or naproxen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. It’s important to use these medications under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
- Modalities: Physical therapists may use modalities such as ice or heat therapy, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation to relieve pain and reduce swelling in the affected knee.
- Activity Modification: Adjusting activities to avoid movements that exacerbate pain or strain on the knee is crucial during the initial phases of non-operative management.

Patient Education and Lifestyle Modifications
Educating individuals about their injury, the importance of compliance with rehabilitation programs, and lifestyle modifications is a fundamental aspect of non-operative management. This involves:
- Understanding the Injury: Providing information about the anatomy of the knee, the role of the ACL, and the specific factors contributing to the injury helps individuals make informed decisions about their care.
- Setting Realistic Expectations: Clearly communicating the expected outcomes of non-operative management, including potential limitations and the importance of ongoing self-care, helps individuals manage their expectations throughout the recovery process.
- Lifestyle Adaptations: Recommending modifications to daily activities, work, or recreational pursuits helps individuals navigate their daily lives while minimizing stress on the injured knee.
- Psychosocial Support: Acknowledging the psychological impact of an ACL tear is crucial. Offering support and resources for coping with the emotional aspects of the injury contributes to a holistic approach to care.
Progress Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular follow-up assessments with healthcare providers and physical therapists are essential to monitor progress, adjust rehabilitation programs, and address any emerging concerns. This ongoing collaboration ensures that individuals receive personalized care tailored to their evolving needs.
FAQ Section
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: Can I return to sports without surgery after an ACL tear?
A: In certain cases, individuals can return to sports or physical activities without surgery, especially with comprehensive rehabilitation and support from healthcare professionals. The decision depends on factors such as the severity of the tear, individual goals, and the type of sports or activities involved.
Q: How long does non-operative management take for ACL tears?
A: The duration of non-operative management varies based on the individual’s progress, adherence to rehabilitation programs, and the nature of the ACL tear. Some individuals may experience significant improvement within a few months, while others may require a more extended rehabilitation period.
Q: Is non-operative management suitable for everyone with an ACL tear?
A: Non-operative management may be suitable for individuals with partial ACL tears, low-demand lifestyles, or those willing to modify their activities. However, the decision depends on various factors, and a thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider is crucial to determine the most appropriate course of action.
Q: Can non-operative management prevent future knee injuries?
A: Comprehensive rehabilitation, including non-operative management strategies, can contribute to improved knee stability, strength, and overall function. Engaging in ongoing strength and flexibility exercises can help reduce the risk of future knee injuries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, navigating the path of non-operative management for ACL tears involves a holistic approach that addresses symptoms, rebuilds strength and stability, and empowers individuals to actively participate in their recovery. With the guidance of skilled healthcare professionals and a commitment to rehabilitation, many individuals can successfully manage ACL tears without surgery, restoring function and regaining confidence in their daily lives. As we traverse the landscape of knee injuries, let us recognize the value of non-operative strategies in fostering comprehensive healing. Let WildHawk Physical Therapy located in Asheville, NC be your partner in healing and getting back to movement pain free!