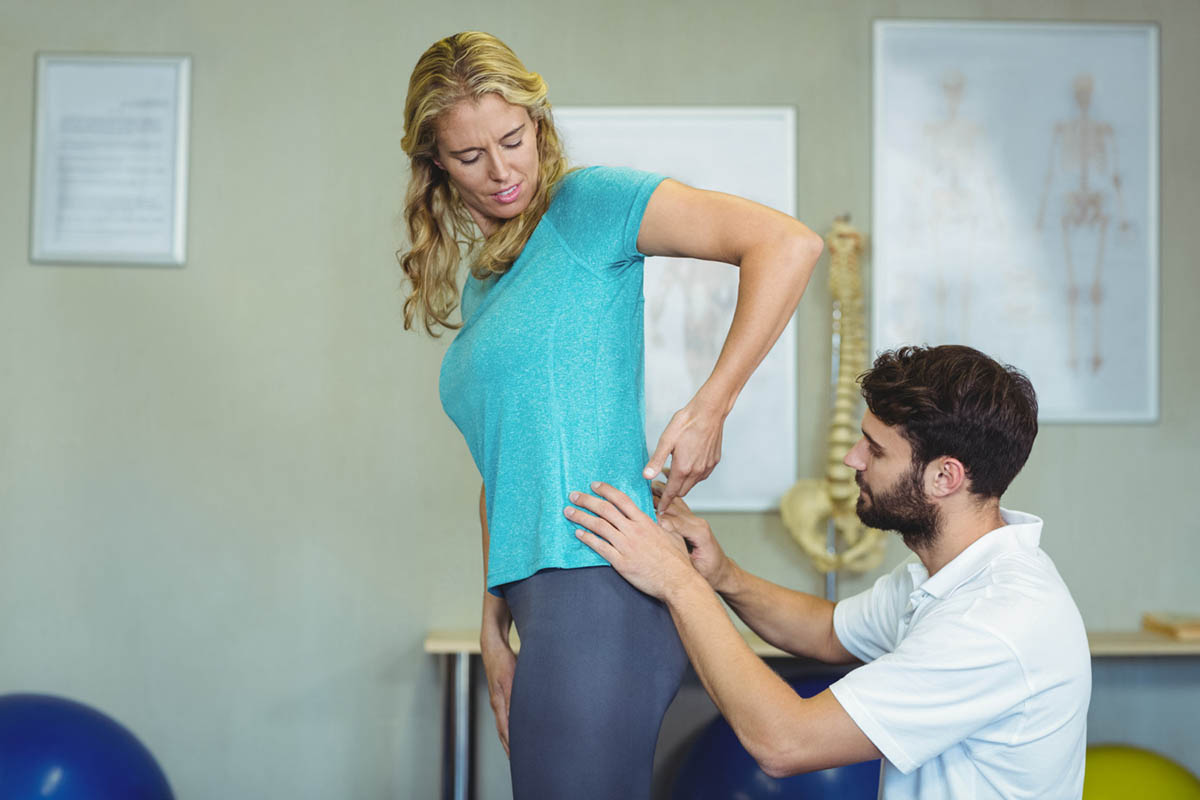
Muscle spasms in back can be a painful and debilitating experience, affecting daily activities and overall quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of these spasms is crucial for effective management and prevention. In this blog, we will look into the reasons behind muscle spasms, how they are diagnosed, and the various treatment options available.
Causes of Muscle Spasms in Back
Muscle spasms in the back can result from various factors. Identifying the underlying cause is essential for proper treatment and prevention.
Muscle Strain
Overuse or sudden movements can lead to muscle strain, which is a common cause of back muscle spasms. Activities like heavy lifting, intense physical activity, or even poor posture can strain the back muscles, causing them to contract involuntarily.
Underlying Anatomical Problems
Issues such as herniated discs, degenerative disc disease, or spinal conditions like ankylosing spondylitis can lead to muscle spasms. These conditions create pressure on nerves and muscles, resulting in painful muscle spasms.
Stress and Tension
Emotional stress and tension can manifest physically, leading to muscle spasms. Psychological conditions cause the body to tighten and contract muscles, particularly in the back, resulting in discomfort and muscle pain.
Dehydration and Electrolyte Imbalance
Proper hydration and balanced electrolytes are essential for muscle function. Dehydration or an imbalance in electrolytes like potassium, calcium, and magnesium can cause muscles to spasm. This imbalance can affect the superficial muscles, intermediate muscles, and spinal muscles, leading to severe pain.
Symptoms of Muscle Spasms in Back
Recognizing the symptoms of muscle spasms can help in early diagnosis and treatment. Here are some of the most common symptoms to look out for.
Sudden Sharp Pain
Muscle spasms often present as a sudden, sharp pain in the affected area. This pain can be intense and debilitating, making it difficult to move or perform normal activities.
Muscle Tightness and Stiffness
The affected muscle may feel tight and stiff, limiting movement and causing discomfort. These tight knots can make even simple movements painful.
Limited Range of Motion
Muscle spasms can restrict the range of motion, making it challenging to perform everyday tasks. This limitation is often due to the tightening of the muscle fibers.
Recurrent or Chronic Discomfort
In some cases, muscle spasms can become a chronic issue, leading to recurrent discomfort and muscle pain. This can significantly impact the quality of life and require ongoing spasm treatment.
Diagnosing Back Muscle Spasms
Accurate diagnosis is key to effective treatment for back muscle spasms. Here’s how healthcare providers typically diagnose muscle spasms in the back.
Medical History and Physical Examination
A thorough medical history and physical examination are the first steps in diagnosing muscle spasms. Doctors will ask about symptoms, activities, and any underlying health conditions like spinal cord issues or spinal conditions.
Diagnostic Tests
In some cases, diagnostic tests such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans may be necessary to identify underlying anatomical problems contributing to muscle spasms. These tests can reveal issues like degenerative disc disease or intervertebral disc abnormalities.
When to See a Specialist
If muscle spasms are severe, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms like numbness, muscle weakness, or loss of bowel control, it’s important to see a spine specialist or a medical professional for further evaluation. These specialists will be able to give you advice on what to do for muscle spasms in back to ensure that you receive proper care and treatment.
Treatment Options for Back Muscle Spasms
There are various treatment options available for managing muscle spasms in the back, ranging from immediate relief to long-term management.
Immediate Relief and First Aid
Rest and Positioning
Resting the affected muscle and maintaining a comfortable position can help alleviate pain and prevent further strain. Using a heating pad or ice pack can also provide immediate spasm relief.
Cold and Heat Therapy
Applying cold packs initially can reduce inflammation and numb the pain. After a few days, switching to heat therapy with a heating pad can help relax the muscles and improve blood flow.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Non-prescription pain relievers like ibuprofen, acetaminophen, and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
Medical Treatments
Prescription Muscle Relaxants
In severe cases, doctors may prescribe muscle relaxants to reduce spasms and alleviate pain. These medications can be particularly helpful when over-the-counter options are not effective.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapists can help strengthen the muscles, improve flexibility, and prevent future spasms. They can also teach exercises to strengthen the core muscles, spinal muscles, and abdominal muscles to support the back.
Injections and Other Medical Interventions
For persistent or severe spasms, corticosteroid injections or other medical interventions may be necessary to reduce inflammation and pain. In some cases, treating underlying conditions like an epidural abscess might be required.
Natural Remedies
Chamomile and Herbal Supplements
Chamomile and other herbal supplements can have relaxing effects on muscles, potentially reducing spasms. These natural remedies can complement traditional treatments for spasm relief.
Dietary Adjustments
Ensuring a balanced diet with adequate hydration and electrolytes can help prevent muscle spasms. Addressing dietary issues and maintaining a healthy weight can also reduce the strain on the back muscles.
Preventing Back Muscle Spasms
Preventative measures can reduce the risk of experiencing muscle spasms in the back.
Regular Exercise and Stretching
Engaging in regular exercise and stretching can strengthen the back muscles and improve flexibility, reducing the risk of spasms. Low-impact activities and aerobic exercise are particularly beneficial.
Proper Hydration and Nutrition
Maintaining proper hydration and a balanced diet with sufficient electrolytes can prevent spasms caused by dehydration or electrolyte imbalances. This includes avoiding dietary issues that can affect muscle function.
Stress Management Techniques
Practicing stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can reduce the physical manifestations of stress, including muscle spasms. Managing mental health issues and emotional health issues is crucial for overall well-being.
Living with Back Muscle Spasms
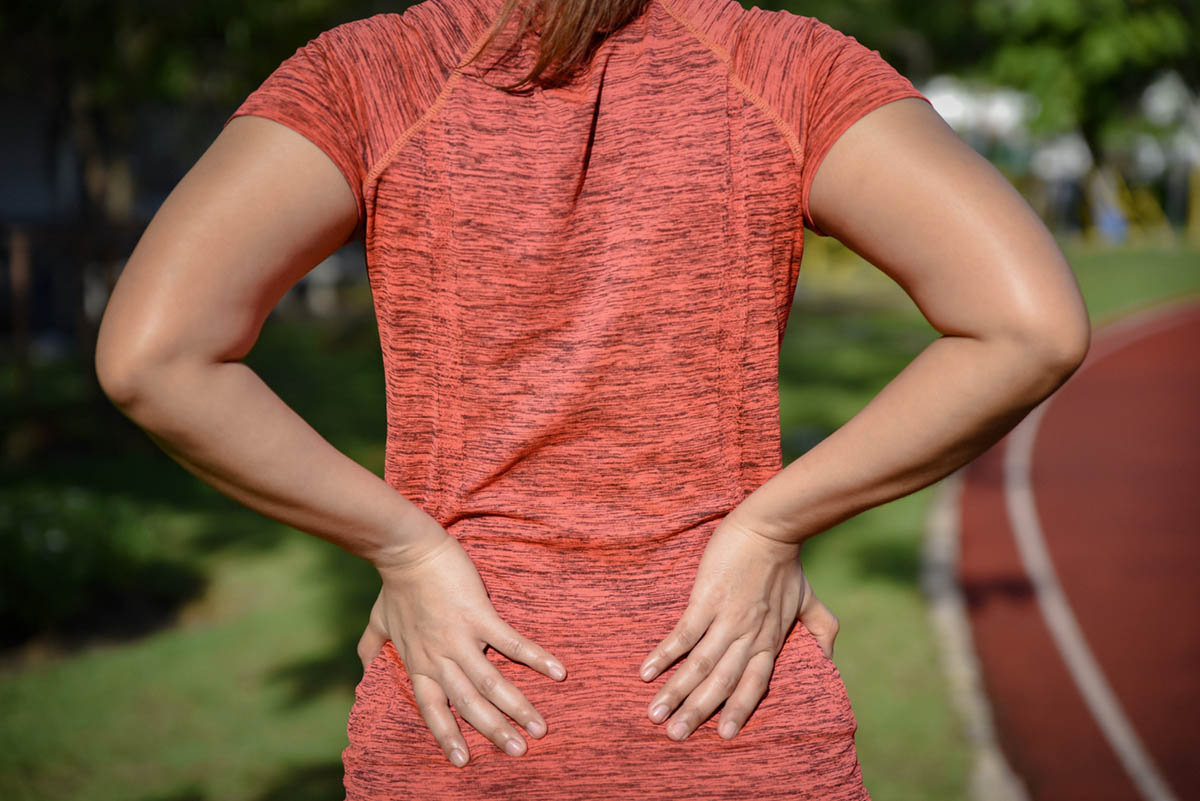

For those who experience chronic muscle spasms, managing symptoms and knowing when to seek help is crucial.
Managing Chronic Muscle Spasms
Chronic muscle spasms require ongoing management, which may include regular physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle adjustments. Chiropractic care and consultation with a healthcare provider can also be part of an effective management plan.
When to Contact a Healthcare Provider
If muscle spasms persist for long periods of time despite treatment, become more frequent, or are accompanied by other concerning symptoms like unexplained weight loss with severe pain, it’s important to contact a healthcare provider as soon as possible.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of muscle spasms in the back can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected. By identifying the underlying causes and implementing appropriate treatments and preventive measures, it is possible to manage and reduce the occurrence of muscle spasms.
At Wild Hawk Physical Therapy, we specialize in treating back pain and lower back pain. Our expert team utilizes advanced diagnostic techniques and personalized treatment plans to alleviate muscle spasms and enhance your overall well-being. Trust WildHawk Physical Therapy for effective relief and a path to a pain-free life.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I get rid of muscle spasms in my back?
Immediate relief can be achieved through rest, cold and heat therapy and over-the-counter pain relievers. For chronic spasms, physical therapy, prescription medications, and lifestyle adjustments may be necessary. Consulting a medical professional for personalized care can also be a great option for treatment.
What is the main cause of back spasms?
Back spasms can be caused by muscle strain, underlying anatomical problems, stress and tension, or dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. Identifying what causes muscle spasms in the back is essential for effective treatment.
How to avoid spasms?
Preventative measures include regular exercise and stretching, proper hydration and nutrition, and stress management techniques. Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding lifting heavy objects improperly can also reduce the risk of spasms.